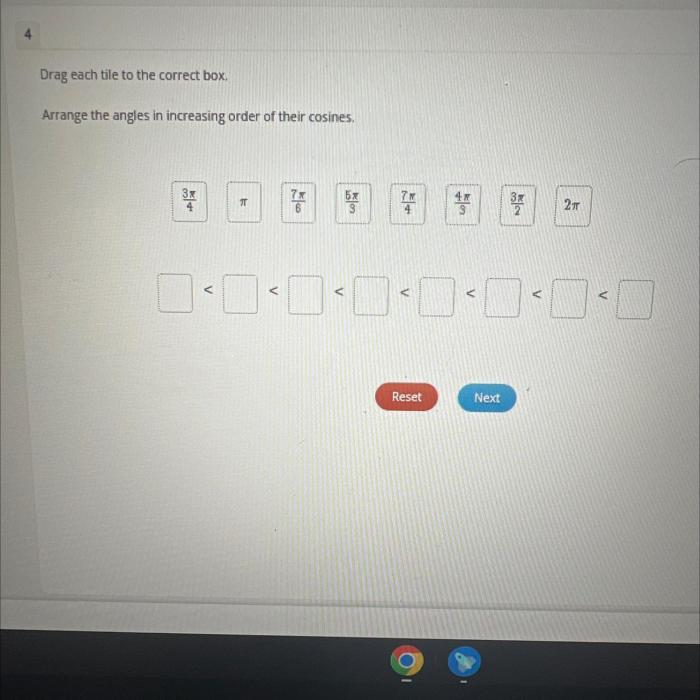
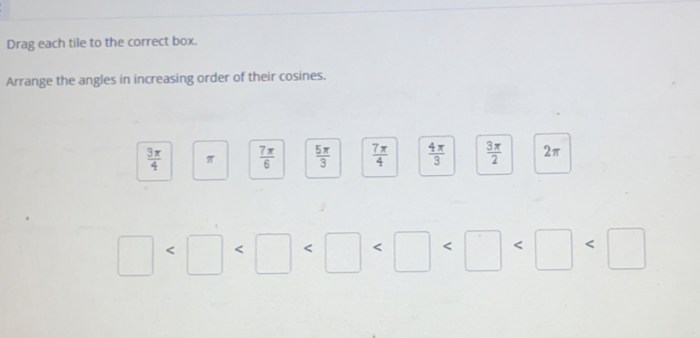
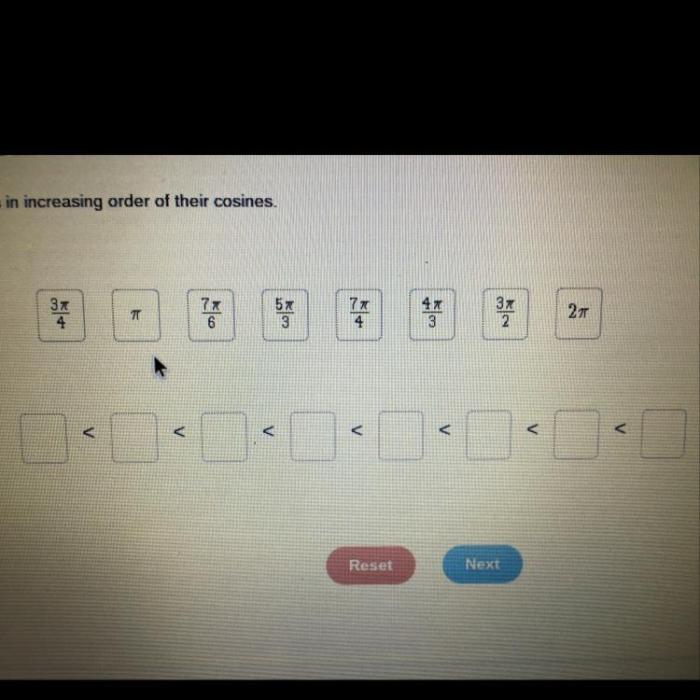
Arrange the angles in increasing order of their cosines – Delving into the fascinating realm of trigonometry, we embark on a journey to understand the concept of cosine and its profound impact on angle measurement. Our exploration culminates in a comprehensive analysis of how angles can be ordered in ascending order of their cosines, revealing the intricate relationship between angles and their trigonometric functions.
Understanding Cosines
The cosine of an angle is a trigonometric function that relates the angle to the ratio of the adjacent side to the hypotenuse in a right triangle. It is defined as the cosine of an angle is the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the length of the hypotenuse.
The cosine of an angle can be calculated using the following formula:
cos(θ) = adjacent side / hypotenuse
Measuring Angles: Arrange The Angles In Increasing Order Of Their Cosines
Angles can be measured in different units, including degrees, radians, and gradians. Degrees are the most common unit of angle measurement, and one degree is defined as 1/360 of a full rotation. Radians are another common unit of angle measurement, and one radian is defined as the angle subtended by an arc of a circle that is equal in length to the radius of the circle.
To convert between degrees and radians, the following formula can be used:
radian = 180 / π degrees
Ordering Cosines
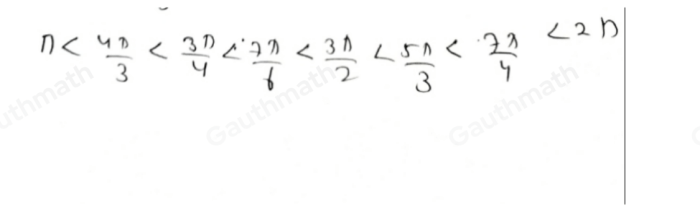
The cosines of angles can be ordered in increasing order of their values. The following table shows the cosines of some common angles:
| Angle (degrees) | Cosine |
|---|---|
| 0 | 1 |
| 30 | √3/2 |
| 45 | √2/2 |
| 60 | 1/2 |
| 90 | 0 |
Applications of Cosine Ordering
Cosine ordering can be used in a variety of fields, including trigonometry, geometry, and physics.
In trigonometry, cosine ordering can be used to solve a variety of problems, such as finding the missing side of a right triangle or finding the angle between two vectors.
In geometry, cosine ordering can be used to determine the area of a triangle or the volume of a cone.
In physics, cosine ordering can be used to calculate the force of gravity between two objects or the trajectory of a projectile.
FAQ Corner
What is the cosine of an angle?
The cosine of an angle is the ratio of the adjacent side to the hypotenuse in a right triangle.
How can I order angles in increasing order of their cosines?
To order angles in increasing order of their cosines, calculate the cosine of each angle and arrange the angles in ascending order based on their cosine values.